
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Adaptive optics techniques have been developed over the past half century and routinely used in large ground-based telescopes for more than 30 years. Although this technique has already been used in various applications, the basic setup and methods have not changed over the past 40 years. In recent years, with the rapid development of artificial intelligence, adaptive optics will be boosted dramatically. In this paper, the recent advances on almost all aspects of adaptive optics based on machine learning are summarized. The state-of-the-art performance of intelligent adaptive optics are reviewed. The potential advantages and deficiencies of intelligent adaptive optics are also discussed.Adaptive optics techniques have been developed over the past half century and routinely used in large ground-based telescopes for more than 30 years. Although this technique has already been used in various applications, the basic setup and methods have not changed over the past 40 years. In recent years, with the rapid development of artificial intelligence, adaptive optics will be boosted dramatically. In this paper, the recent advances on almost all aspects of adaptive optics based on machine learning are summarized. The state-of-the-art performance of intelligent adaptive optics are reviewed. The potential advantages and deficiencies of intelligent adaptive optics are also discussed.
adaptive optics machine learning deep learning Opto-Electronic Advances
2022, 5(7): 200082
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
在地基太阳观测中,光线在穿越大气层时会受到大气湍流的影响而导致图像扭曲、变形以致质量下降。为了消除或降 低大气湍流的影响,事后图像处理技术被用来获得高分辨力的太阳图像。基于斑点干涉法和斑点掩模的事后重建算 法可以获得高分辨力的图像,但由于计算复杂度高,难以满足实时性的要求。在讨论了算法原理的基础上, 使用CUDA并行计算架构实现了太阳斑点重建算法并行化。实验结果表明,在GPU环境下,一张TiO通 道2304 pixel×1984 pixel像素大小的图像,可以在70 s内完成重建,相比运行在CPU上的串行程序,加速比可达7以上。
图像重建 斑点干涉法 斑点掩模法 并行计算 GPU GPU CUDA CUDA image reconstruction speckle interferometry speckle masking parallel computing
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
对太阳大气进行大视场高分辨力光学成像观测是开展太阳物理、空间天气等基础与应用研究的重要前提。对于地基太阳望远镜而言,为了消除地球大气湍流对光学系统的影响,自适应光学是高分辨力成像观测必备的技术手段,与此同时,为了突破大气非等晕性对传统自适应光学校正视场的限制,近年来多层共轭自适应光学技术等大视场自适应光学得到极大发展。本文首先梳理国外太阳自适应光学系统研制情况,重点介绍国内太阳自适应光学技术发展及应用情况,并进一步介绍了后续大视场太阳自适应光学技术发展情况以及目前所取得的成果。
太阳观测 自适应光学 多层共轭自适应光学 solar observation adaptive optics multi-conjugate adaptive optics
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室,四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所,四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
为进一步提高自适应光学系统的成像质量,本文针对目前广泛使用的盲解卷积,相位差法和斑点重建技术开展了深入研究;详细分析了以上三种技术的各自特点、应用场景和处理对象,并结合自适应光学系统的特点,有针对性的加以算法改进;实验采用自适应光学人眼视网膜细胞图像和自适应光学太阳黑子图像进行算法验证,结果表明经改进后的图像处理技术可以有效提高自适应光学图像的质量和分辨力,较好的满足了自适应光学系统对图像事后处理的需求。
自适应光学 图像重建 盲解卷积 相位差法 斑点重建 adaptive optics image reconstruction blind deconvolution phase diversity speckle imaging
1 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
地基太阳高分辨力成像中,自适应光学系统补偿了图像中心等晕区的像差,需要斑点图像重建技术用来产生全视场衍射极限分辨率的图像。一个从Matlab程序移植而来的C语言程序被设计用于加速处理。该程序采用斑点干涉法重建图像的傅里叶振幅和斑点掩膜法重建图像的傅里叶相位。使用OpenMP进行加速,使核心间共享了部分内存资源,图像按子块进行并行计算。移植过程中程序算法上进行了必要的优化并移除了大量的冗余计算。程序使用英特尔ICC编译器编译,运行在一个12核的Linux服务器上。一张1280 pixel×1280 pixel的图像可以在31 s内重建完成。相对于单核运行,加速比最高可以达到10.66。单台服务器上相对于并行接口获得更好的扩展性。
图像处理 图像重建技术 斑点干涉法 斑点掩膜法 并行计算 激光与光电子学进展
2017, 54(6): 061001
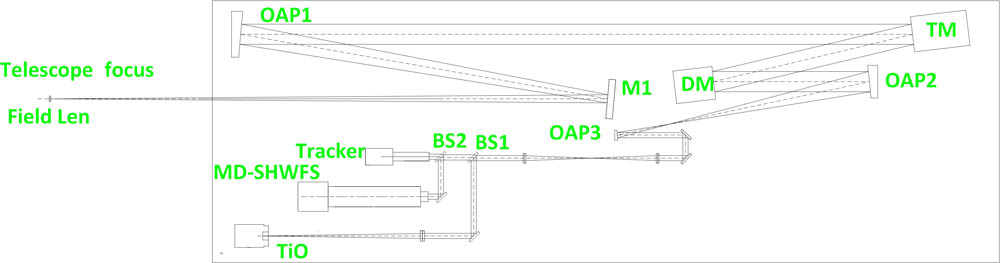
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Key Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
2 The Laboratory on Adaptive Optics, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
A prototype of a solar ground-layer adaptive optics (GLAO) system, which consists of a multi-direction correlating Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor with 30 effective subapertures and about a 1 arcmin field of view (FoV) in each subaperture, a deformable mirror with 151 actuators conjugated to the telescope entrance pupil, and a custom-built real-time controller based on field-programmable gate array and multi-core digital signal processor (DSP), is implemented at the 1 m New Vacuum Solar Telescope at Fuxian Solar Observatory and saw its first light on January 12th, 2016. The on-sky observational results show that the solar image is apparently improved in the whole FoV over 1 arcmin with the GLAO correction.
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.1080 Active or adoptive optics Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 100102
1 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 四川 成都 610209
2 中国科学院自适应光学重点实验室, 四川 成都 610209
3 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
斑点图像重建方法可以有效抑制大气湍流的影响,得到目标衍射极限像。然而系统静态像差破坏了波前的统计信息,降低了相位重建精度。通过理论分析得出在理想情况下,离焦、像散、彗差和球差中只有彗差会在重建结果中引入额外相位值。进一步采用分割光瞳的方式表示交叉谱传递函数与静态像差的关系时,指出通过选择交叉谱的平移向量方向,可以实现在特定方向上静态像差之间的平衡,降低系统像差对相位重建的影响。仿真中球差与离焦像差之间的平衡及离焦像差与像散之间的平衡,都起到了降低相位重建误差的效果。
大气光学 图像处理 静态像差 斑点干涉





